Getting Started
This topic introduces Data Profiler and describes key data profiling concepts.
Data profiling involves examining a dataset to detect any inconsistencies, anomalies, and invalid entries. A crucial component of this process is the implementation of profiling rules. These rules are designed to define what constitutes valid and invalid values within the data. By establishing these guidelines, users can ensure that the dataset adheres to specific values, standards, or patterns. This structured approach not only aids in maintaining the integrity of the data but also supports adherence to data quality standards.
Data Profiler provides many rules which are designed to identify various data quality issues (see Rule and Parameter Reference). Multiple rules can be applied to a single field, allowing the user to check or enforce multiple conditions for a single field.
Profile rules can be configured to enforce specific conditions or values. When a rule is applied to a specific field in a profile, the data in that field is evaluated against the condition or value within the rule. After processing is complete, each value from the source field is categorized as either valid or invalid. Valid data is written to the Pass target, while invalid data is written to the Fail target. Data in the Pass target can be processed or used immediately, while the data in the Fail target can be routed for remediation (see Define Targets and Results).
Data is evaluated based on the conformance to the conditions or values defined within the profile rules. The rules specify characteristics such as accuracy, completeness, consistency, timeliness, validity, and uniqueness. Once data has been profiled, multiple views are provided which help identify data quality issues and trends (see Run History).
Data Profiler has two main environments: Design and Manage. Typically, you create, test, refine, and schedule data profiles in the Design environment. Then execute, monitor, and manage job execution results in the Manage environment.
The following figure illustrates the Data Quality console pages that open by default in each environment.
Design Environment | Manage Environment | |
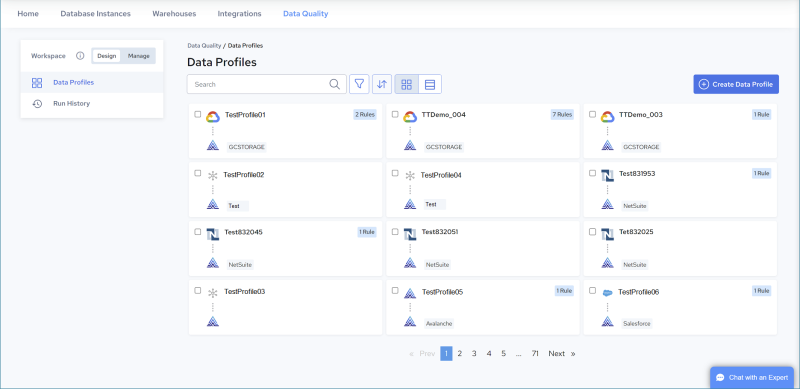 | 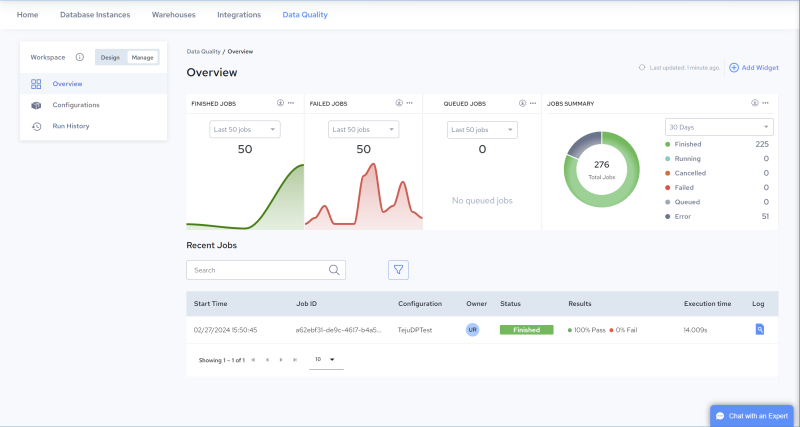 | |
Data Profiles Page Create, Edit, Test & Schedule Profiles | Overview Page Monitor Job Results Edit & Manage Configurations |
Use the Design environment to establish a connection (see Source and Target Connections). Then use it to create a data profile by defining a source (see Define Source), creating data quality rules (see Define Rules and Analyze Results), and defining a target (see Define Targets). Data isn’t persisted until the targets are configured within the profile.
Data profiles can be executed manually (see Run a Profile Manually) or scheduled to execute (see Edit Profile Schedule). To gain insight into overall execution results, see Run History for all Profiles. To investigate results per profile, see View Profile Details.
For a list of available sources, see Source and Target Connections. Actian Warehouse can be used as the target.
Use the Manage environment to schedule and execute profiles using the associated configuration (see Managing Configurations), gain insight into overall execution results (see Run History), investigate results per profile and rule (see Run History for a Single Configuration), and monitor overall execution results in the Manage, Overview Page.
Last modified date: 12/17/2025