Universal Unique Identifier (UUID)
A Universal Unique Identifier (UUID) is a 128 bit, unique identifier generated by the local system. It is unique across both space and time with respect to the space of all UUIDs.
A UUID can be used to tag records to ensure that the database records are uniquely identified regardless of which database they are stored in, for example, in a system where there are two separate physical databases containing accounting data from two different physical locations.
No centralized authority is responsible for assigning UUIDs. They can be generated on demand (10 million per second per machine if needed).
A UUID can be used for multiple purposes:
• Tagging objects that have a brief life
• Reliably identifying persistent objects across a network
• Assigning as unique values to transactions as transaction IDs in a distributed system
UUIDs are fixed sized (128 bits), which is small relative to other alternatives. This fixed small size lends itself well to sorting, ordering, and hashing of all sorts, sorting in databases, simple allocation, and ease of programming.
UUID Format
The format of 128-bits (16 octets) UUID is:
Field | Data Type | Octet Number | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
time_low | unsigned 32-bit integer | 0-3 | The low field of the timestamp |
time_mid | unsigned 16-bit integer | 4-5 | Time middle field of the timestamp |
time_hi_and_version | unsigned 16-bit integer | 6-7 | The high field of the timestamp multiplex with the release number |
clock_seq_hi_and_reserved | unsigned 8-bit integer | 8 | The high field of the clock sequence multiplex with the variant |
clock_seq_low | unsigned 8-bit integer | 9 | The low field of the clock sequence |
node | unsigned 48-bit integer | 10-15 | The spatially unique node identifier |
UUID Functions
Ingres implements the following SQL procedures to create, convert, and compare UUIDs:
• UUID_CREATE( )
• UUID_COMPARE(uuid1, uuid2)
• UUID_TO_CHAR(u)
• UUID_FROM_CHAR(c)
UUID_CREATE( ) Function
The UUID_CREATE() function creates a 128 bit UUID:
> createdb uuiddb
> sql uuiddb
* CREATE TABLE uuidtable (u1 BYTE (16), u2 BYTE(16));
* INSERT INTO uuidtable VALUES (UUID_CREATE(), UUID_CREATE());
//
// Verify the length in byte format
//
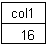
* SELECT LENGTH(u1) FROM uuidtable;
//
//Length returned equals 16 bytes
//
UUID_COMPARE(uuid1, uuid2) Function
The UUID_COMPARE(uuid1, uuid2) function returns an integer value:
Return | Meaning |
|---|---|
-1 | uuid1 < uuid2 |
0 | uuid1 == uuid2 |
+1 | uuid1 > uuid2 |
//
// Determine if u1 is greater than, less than, or equal to u2
//
* SELECT UUID_COMPARE(u1, u2) FROM uuidtable;
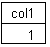
//
// u1 > u2
//
UUID_TO_CHAR(u) Function
The UUID_TO_CHAR(u) function converts a generated UUID into its character representation.
* SELECT UUID_TO_CHAR(u1) FROM uuidtable;

//
// Verify length of UUID in character format
//
* SELECT LENGTH(UUID_TO_CHAR(u1)) FROM uuidtable;
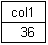
//
//A UUID contains 36 characters
//
UUID_FROM_CHAR(c) Function
The UUID_FROM_CHAR(c) function converts a UUID from its character representation into byte representation:
//
// Insert a UUID in character format into a table
//
* CREATE TABLE uuidtochar
* CREATE TABLE uuidtochar
AS
SELECT UUID_TO_CHAR(u1) AS c1 FROM uuidtable;
* SELECT c1 FROM uuidtochar;

//
// convert UUID into byte representation
//
* SELECT UUID_FROM_CHAR(c1) FROM uuidtochar;
// convert UUID into byte representation
//
* SELECT UUID_FROM_CHAR(c1) FROM uuidtochar;

Last modified date: 07/21/2025