Components of IMA
The IMA architecture is represented in the following diagram:
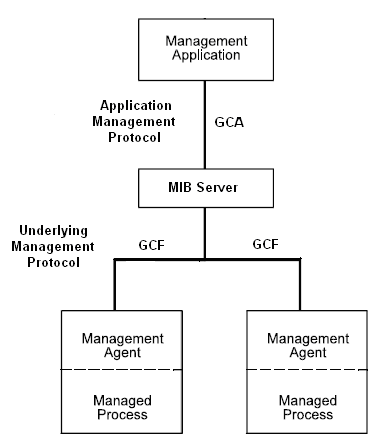
The user interfaces with an SQL-based Management Application program, for example, OpenROAD.
The Management Application interfaces with the MIB Server across the Application Management Protocol. Ingres has its own communications protocol that uses the GCA (General Communications Architecture).
GCA is the communications interface used by clients, servers, and distributed data managers to access GCF services that passed tuples, queries, and commands between Ingres processes. Through this mechanism, the Management Application receives MIB data from the MIB Server.
In the current IMA architecture, a MIB Server is a DBMS server.
The GCA allows the Management Application to either connect directly to a MIB Server or indirectly to a remote MIB Server using a GCC process.
The IMA components in the MIB Server are as follows:
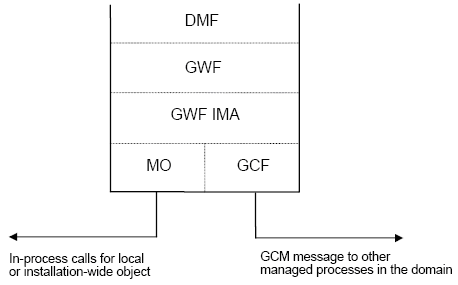
Component | Description |
|---|---|
DMF | Data Management Facility |
GWF | Gateway (Enterprise Access) Facility |
IMA GWF | IMA Gateway Facility |
MO | Managed Object module for handling local DBMS IMA objects |
GCF | General Communication Facility for communicating with other Ingres processes |
GCM | General Communication Mechanism for communicating with other Ingres processes |
The MIB Server uses IMA GWF, a non-relational gateway to present the IMA objects as relational database tables.
Without a MIB Server, IMA data is not available to ordinary users.
For objects internal to the DBMS Server, the MIB Server reads and writes objects directly through MO. Objects in other processes, for example a Communications Server, are handled using the GCF message protocol.
A Managed Process only needs to talk a single protocol, while MIB servers can support Management Applications using a variety of protocols.
IMA has been designed to be compatible with other management protocols, for example:
• SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)
• DME (Distributed Management Environment)
• CMIP (Common Management Interface Protocol)
Last modified date: 08/28/2024