COPY Examples
The following examples illustrate various features of the COPY statement.
Example 1:
In the following example, the contents of the file "emp.txt" are copied into the "employee" table. A dummy column is used to omit the "city" column. The format of the" employee" table is as follows:
ename char(15)
age integer4
dept char(10)
comment varchar(20)
age integer4
dept char(10)
comment varchar(20)
The "emp.txt" file contains the following data:
Jones,J. 32 Anytown,USA toy,00017A comment
Smith,P. 41 New York,NY admin,00015Another comment
Smith,P. 41 New York,NY admin,00015Another comment
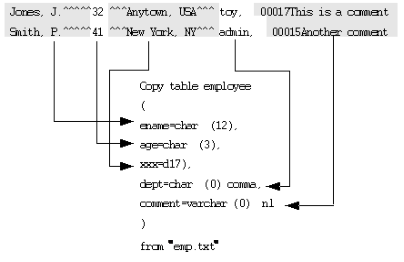
The following diagram illustrates the copy statement that copies the file "emp.txt" into the employee table and maps the fields in the file to the portions of the statement that specify how the field is to be copied. Note the following points:
• A dummy column is used to skip the city and state field in the data file, because there is no matching column in the employee table.
• The "department" field is delimited by a comma.
• The "comment" field is a variable-length varchar field, preceded by a five-character length specifier.
Example 2:
Load the "employee" table from a data file. The data file contains binary data (as opposed to character data that can be changed using a text editor):
copy table employee (eno=integer2, ename=char(10),
age=integer2, job=integer2, sal=float4,
dept=integer2, xxx=d1)
from "myfile.in"
age=integer2, job=integer2, sal=float4,
dept=integer2, xxx=d1)
from "myfile.in"
Example 3:
Copy data from the "employee" table into a file. The example copies employee names, employee numbers, and salaries into a file, inserting commas and newline characters so that the file can be printed or edited. All items are stored as character data. The "sal" column is converted from its table format (money) to ASCII characters in the data file.
copy table employee (ename=char(0)tab,
eno=char(0)tab, sal= char(0)nl)
into "myfile.out"
eno=char(0)tab, sal= char(0)nl)
into "myfile.out"

Example 4:
Bulk copy the "employee" table into a file. Resulting data file contains binary data:
copy table employee () into "ourfile.dat"
Example 5:
Bulk copy from the file created in the preceding example:
copy table other_employee_table () from "ourfile.dat"
Example 6:
Copy the "acct_recv" table into a file. The following statement skips the address column, uses the percent sign (%) as a field delimiter, uses "xx" to indicate null "debit" and "credit" fields, and inserts a newline at the end of each record:
copy table acct_recv
(acct_name=char(0)"%",
address="d0%",
credit=char(0)"%" with null("xx"),
debit=char(0)"%" with null("xx"),
acct_mngr=char(15),
nl=d1)
into "qtr_result";
(acct_name=char(0)"%",
address="d0%",
credit=char(0)"%" with null("xx"),
debit=char(0)"%" with null("xx"),
acct_mngr=char(15),
nl=d1)
into "qtr_result";

Example 7:
Copy a table called "gifts" to a file for archiving. This table contains a record of all non-monetary gifts received by a charity foundation. The columns in the table contain the name of the item, when it was received, and who sent it. Because givers are often anonymous, the column representing the sender is nullable.
copy table gifts
(item_name=char(0)tab,
date_recd=char(0)tab,
sender=char(20)nl with null("anonymous"))
into "giftdata";
(item_name=char(0)tab,
date_recd=char(0)tab,
sender=char(20)nl with null("anonymous"))
into "giftdata";

Last modified date: 02/26/2025