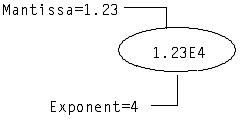

Range of Binary Precision | Storage Allocated | Example |
0 to 23 | 4-byte float | float(18) defines a floating point type with at least 18 binary digits of precision in the mantissa. A 4‑byte floating point field is allocated for it, which has 23 bits of precision. |
24 to 53 | 8-byte float | float(41) defines a floating point type with at least 41 binary digits of precision in the mantissa. A 8‑byte floating point field is allocated for it, which has 53 bits of precision. |