Quick Start
The following basic information enables you to connect to a database using the PSQL ADO.NET data providers immediately after their installation:
To take full advantage of PSQL ADO.NET data provider features, we recommend that you also read other ADO.NET topics documented here.
Supported .NET Framework Versions
The following table lists the PSQL data providers supported for use with Microsoft .NET Framework and Microsoft Entity Framework. Each row of the table represents the compatible combinations of versions of these three products.
PSQL Provider | Microsoft .NET Framework | Microsoft Entity Framework |
ADO.NET Data Provider 4.2 | 2.0, 3.0, 3.5, 3.5 SP1, 4.0, 4.5, 4.5.1, 4.5.2, 4.6, 4.6.1, 4.6.2 | — |
ADO.NET Data Provider 4.3 | 2.0, 3.0, 3.5, 3.5 SP1, 4.0, 4.5, 4.5.1, 4.5.2, 4.6, 4.6.1, 4.6.2 | — |
ADO.NET Entity Framework Provider 4.2 | 4.5, 4.5.1, 4.5.2, 4.6.1, 4.6.2 | 5.0 |
ADO.NET Entity Framework Provider 4.3 | 4.5, 4.5.1, 4.5.2, 4.6.1, 4.6.2 | 5.0 |
ADO.NET Entity Framework Provider 4.2.0.6 | 4.5, 4.5.1, 4.5.2, 4.6.1, 4.6.2 | 6.0, 6.0.1, 6.0.2 |
ADO.NET Entity Framework Provider 4.3.0.6 | 4.5, 4.5.1, 4.5.2, 4.6.1, 4.6.2 | 6.0, 6.0.1, 6.0.2, 6.1, 6.1.1, 6.1.2 |
The PSQL ADO.NET Entity Framework data provider supports three versions of the Microsoft Entity Framework: 5.0, 6.0, and 6.1.
All versions listed apply to both 32- and 64-bit versions of .NET Framework.
If you are using ADO.NET without customization, then code written for earlier versions of the .NET Framework and of the PSQL data provider is compatible with PSQL data provider 4.2 and 4.3.
To use PSQL ADO.NET Entity Framework 4.2 and 4.3, your applications must target .NET Framework 4.5 or later.
Microsoft Entity Framework 6.1, 6.1.1, are 6.1.2 are compatible only with PSQL ADO.NET Entity Framework Provider 4.3.0.6.
Defining Basic Connection Strings
The data provider uses a connection string to provide information needed to connect to a specific database server. The connection information is defined by connection string options.
The ADO.NET Entity Framework data provider can specify an existing connection in the Entity Framework Wizard, or can define a new connection. The ADO.NET Entity Framework uses information contained in connection strings to connect to the underlying ADO.NET data provider that supports the Entity Framework. The connection strings also contain information about the required model and mapping files. The data provider uses the connection string when accessing model and mapping metadata and connecting to the data source.
The connection string options have the form:
"option name=value"
Each connection string option value pair is separated by a semicolon. For example,
"Server DSN=DEMODATA;UID=test;PWD=test;Host=localhost"
See Table
27 for detailed information about all of the supported connection string options.
Notes
•The spaces in the option names are optional.
•All connection string option names are case-insensitive. For example, User ID is the same as user id. However, the values of some options, such as User ID and Password, might be case-sensitive.
•If the connection string does not specify a port number, the data provider uses 1583, the default port number.
Table
1 gives the name and description for each option required for a minimum connection to a PSQL server.
Table 1 Minimum Connection String Options Required
Option | Description |
Server DSN | Specifies the name of the data source on the server to which you want to connect, for example, DEMODATA. |
Host | Specifies the name or the IP address of the PSQL server to which you want to connect. For example, you can specify a server name such as Accountingserver or an IP address such as 199.226.22.34 (IPv4) or 1234:5678:0000:0000:0000:0000:9abc:def0 (IPv6). The initial default value is localhost. |
Connecting to a Database
Once your data provider is installed, you can connect from your application to your database with a connection string. See Table
27 for a list of the connection string options.
Note: If your application uses the ADO.NET Entity Framework, you can use the Entity Data Model Wizard to create a new connection or use an existing connection. See
Creating a Model for more information.
Example: Using the Provider-Specific Objects
The following example uses the provider-specific objects to connect to a database using the ADO.NET data provider from an application developed in Visual Studio using C#.
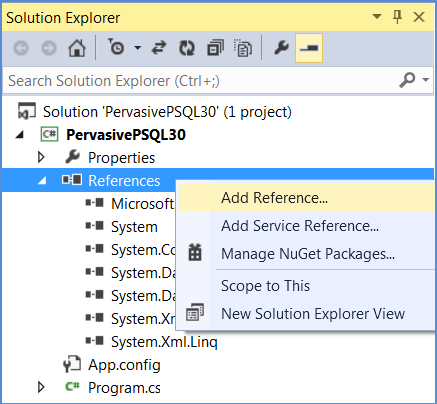
1 In the Solution Explorer, right-click References and then select Add Reference.
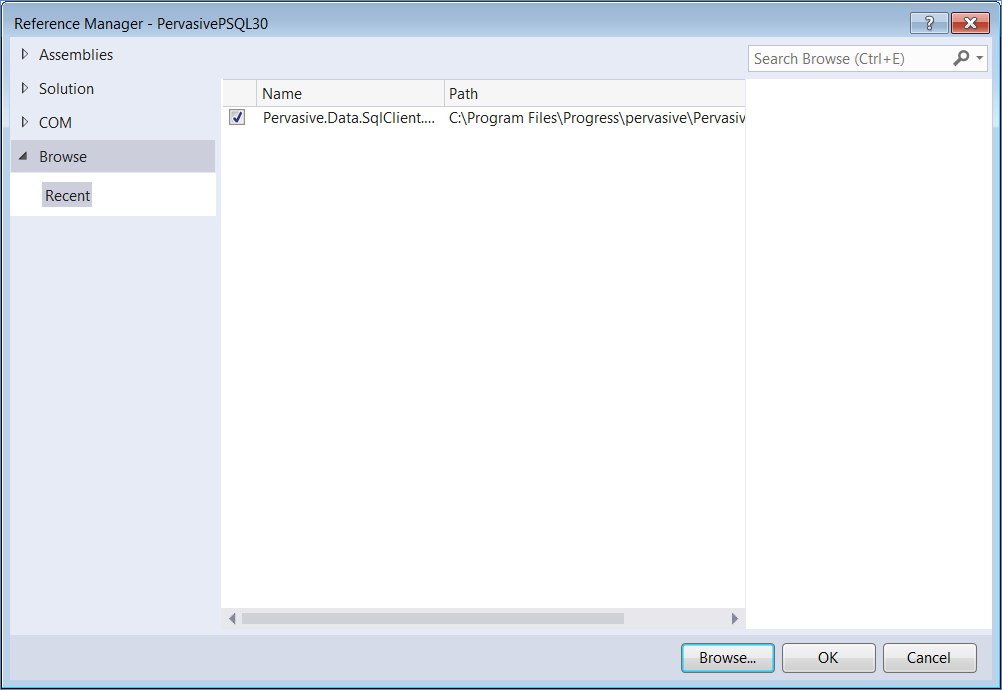
2 In the Reference Manager wizard, click the Browse button and navigate to the folder that contains the PSQL data provider assembly.
3 Select Pervasive.Data.SqlClient.dll and click Add. The Browse tab of the Reference Manager wizard lists the PSQL data provider assembly in the Recent items.
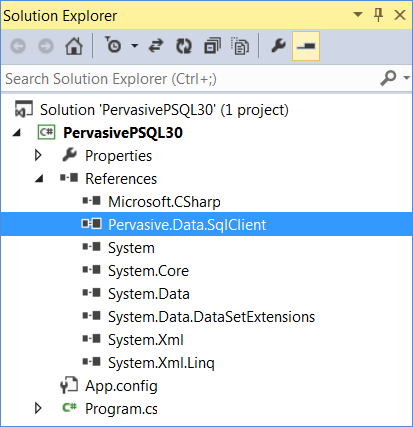
4 Select it and click OK. The Solution Explorer now includes the PSQL data provider.
5 Add the PSQL data provider’s namespace to the beginning of your application, as shown in the following C# code fragment:
// Access PSQL
using System.Data;
using System.Data.Common;
using Pervasive.Data.SqlClient;
6 Add exception handling code and the connection information for your server:
PsqlConnection DBConn = new PsqlConnection("Server DSN=DEMODATA;Host=localhost");
try
{
// Open the connection
DBConn.Open();
Console.WriteLine("Connection Successful!")
}
catch (PsqlException ex)
{
// Connection failed
writer.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
7 Close the connection.
// Close the connection
DBConn.Close();
Example: Using the Common Programming Model
The following example illustrates connecting to a PSQL database from an application developed in Visual Studio using C# and the Common Programming Model.
1 Check the beginning of your application. Ensure that the ADO.NET namespaces are present.
// Access PSQL using factory
using System.Data;
using System.Data.Common;
2 Add the connection information of your server and exception handling code and close the connection.
DbProviderFactory
factory=DbProviderFactories("Pervasive.Data.SqlClient");
DbConnection Conn = factory.createConnection();
Conn.CommandText = "Server DSN=DEMODATA;Host=localhost;";
try
{
Conn.Open();
Console.WriteLine("Connection successful!");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// Connection failed
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
// Close the connection
Conn.Close();
Example: Using the PSQL Common Assembly
You can optionally include the PSQL Common Assembly if you want to use features such as PSQL Bulk Load in an application that conforms to the Common Programming Model. See
Using PSQL Bulk Load for information about how to use PSQL Bulk Load with your application.
The following example illustrates how to use the PSQL Common Assembly in an application developed in Visual Studio using C# and the Common Programming Model.
1 Check the beginning of your application. Ensure the .NET Framework and PSQL data provider namespaces are present.
// Access PSQL using factory
using System.Data;
using System.Data.Common;
using Pervasive.Data.Common;
2 Add the connection information of your server and exception handling code and close the connection.
// This code does a bulk copy operation from one
// PSQL database to another
DbProviderFactory Factory = DbProviderFactories.GetFactory("Pervasive.Data.SqlClient");
DbConnection sourceConnection = Factory.CreateConnection();
sourceConnection.ConnectionString = "Host=localhost;Server DSN=DEMODATA;";
sourceConnection.Open();
DbCommand command = sourceConnection.CreateCommand();
command.CommandText = "SELECT * FROM test";
DbDataReader reader = command.ExecuteReader();
DbConnection destinationConnection = Factory.CreateConnection();
destinationConnection.ConnectionString =
"Host= ntsl2003b;Server DSN=DEMODATA";
destinationConnection.Open();
DbBulkCopy bulkCopy = new DbBulkCopy(destinationConnection);
bulkCopy.DestinationTableName = "test";
try
{
bulkCopy.WriteToServer(reader);
}//end try
catch (DbException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine( ex.Message );
}//end catch
finally
{
reader.Close();
MessageBox.Show("done");
}//end finally
Using the ADO.NET Entity Framework Data Provider
The Entity Data Model wizard asks questions that help you to define the components in your Entity Data Model (EDM). The wizard then creates a model of your data in Visual Studio, and automatically sets values for the components in the model. See
Using an .edmx File for information about using the wizard to create an EDM.
Alternatively, you can use other tools in Visual Studio to define values and connection strings manually.
Provider is an attribute of the Schema element in the storage model file of an EDM. The storage model file is written in the store schema definition language (SSDL).
The Entity Data Model wizard assigns the value when you select the PSQL ADO.NET Entity Framework data provider. If you choose to manually define an Entity Data Model, assign the string Pervasive.Data.SqlClient to the Provider attribute of the Schema element, as shown in the following example:
<Schema Namespace="AdventureWorksModel.Store" Alias="Self" Provider="Pervasive.Data.SqlClient" ProviderManifestToken="PSQL" xmlns:store="http://schemas.microsoft.com/ado/2007/12/edm/EntityStoreSchemaGenerator" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/ado/2006/04/edm/ssdl">