Troubleshoot Startup, Shutdown, or Configuration Problems
Use the following flow chart to isolate a problem with startup, shutdown or configuration of your Vector installation:
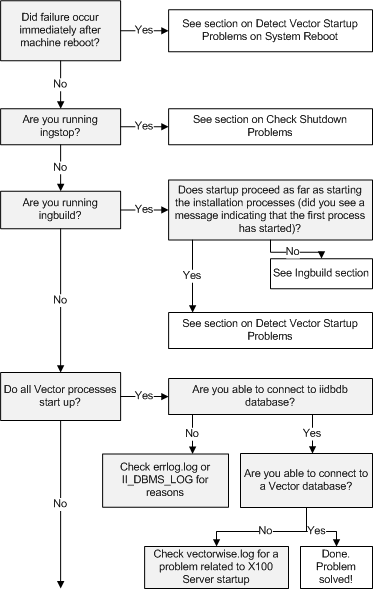
Check Vector Installation on Windows
To check if the installation is working fine, follow these steps:
1. Check that you are logged in as the installation owner. If not, log off and log in again as this user.
2. Check that all users have II_SYSTEM set by issuing the following command at the operating system prompt:
echo %II_SYSTEM%
All users must have Vector executables in their path variables. Check that everyone has the full search path to %II_SYSTEM%\ingres\bin.
The installation owner must also include %II_SYSTEM%\ingres\utility.
3. Check that each of the Vector variables has a valid value.
Vector environment variables are only used and “seen” by Vector and can be displayed with the following command entered at the operating system prompt:
ingprenv
If you are in doubt about the function or legal value of a particular environment variable, see the chapter on setting environment variables and the appendix on environment variables.
Vector environment variables denoting installation locations cannot be reset. To change these, you must unload the databases, rerun the installation program, and reload the databases, as described in Installation Locations.
4. Check the Vector environment variables that have been set locally, overriding the installation-level definitions.
Only a small category of Vector environment variables must be defined in the local user environment: those that permit you to access Vector, and those that define values that are different for your local environment. They include TERM_INGRES and ING_EDIT.
If you trace the problem to a Vector environment variable setting, correct the value. For procedures and scenarios for setting these environment variables, see the chapter on setting environment variables. If the installation does not start up, continue with this procedure.
5. Check that all Vector processes are shut down. If there are processes that continue to run, see the section Check Shutdown Problems on Windows.
6. Restart Vector. Attempt once again to start up the installation by issuing the following command at the operating system prompt:
ingstart
If startup problems persist, continue diagnostics in the Detect Startup Problems section.
Detect Vector Startup Problems on Windows
To troubleshoot startup problems on Windows, follow these steps:
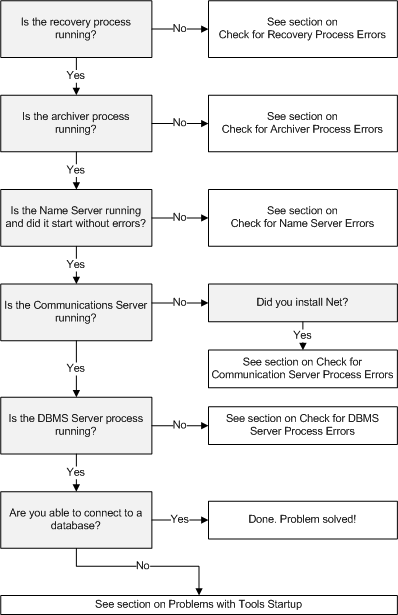
1. Determine which Vector processes are running.
2. Verify that all required Vector system processes are running. The following processes are the minimum required for a complete installation:
iigcn
Name Server process
iigcc
Communications Server process (present only on sites with Ingres Net)
II_IUSV_nnn
Recovery Server process
dmfacp
Archiver process
iidbms
DBMS Server process
iigcd
Data Access Server process
rmcmd
Remote command process
3. If ingstart does not complete successfully, do the following:
g. Check the output from ingstart. This is saved in the file:
%II_SYSTEM%\ingres\files\ingstart.log
Error log files and individual component log files are listed in Logging and Locking Systems.
h. Try to determine the reason for startup failure.
i. A process failed to start. If a process failed to start, continue on to the detailed sections on startup problems for that specific process.
Check Vector Installation on Linux
To check if the Vector installation is working fine, follow these steps:
1. Check that you are logged in as the installation owner by issuing the following command at the operating system prompt:
whoami
If the user ID of the installation owner is not shown, log off and log in again as this user.
2. Check that all users have II_SYSTEM set by issuing the following command at the operating system prompt:
echo $II_SYSTEM
/ usr/r6 (this varies by system)
All users must have Vector executables in their path variables. Check that everyone has the full search path to II_SYSTEM/ingres/bin.
The installation owner must also include II_SYSTEM/ingres/utility.
3. Check that each of the Vector installation variables has a valid value.
Vector environment variables are only used and “seen” by Vector and can be displayed with the following command entered at the operating system prompt:
ingprenv
If you are in doubt about the function or legal value of a particular environment variable, see the chapter "Setting Environment Variables" and the appendix "Environment Variables."
Vector environment variables denoting installation locations cannot be reset. To change these, you must rerun the installation program, ingbuild, and on Linux possibly unload and reload your database with unloaddb. More information is provided in Installation Locations.
4. Check the Vector environment variables that have been set locally, overriding the Vector installation-level definitions. Issue the following commands at the operating system prompt:
BSD:
printenv | grep II
printenv | grep ING
System V:
env | grep II
env | grep ING
Only a small category of Vector environment variables must be defined in the local user environment: those that permit you to access Vector, and those that define values that are different for your local environment. They include TERM_INGRES and ING_EDIT.
If you trace the problem to a Vector environment variable setting, correct the value. For details, see "Setting Environment Variables." If the installation does not start up, continue with this procedure.
5. Identify your installation code. If there is more than one Vector installation on this machine, type the following command at the operating system prompt. The installation code is used to distinguish which processes belong to which installation at sites with more than one Vector installation on the same machine:
ingprenv | grep II_INSTALLATION
The two-letter installation code is displayed (for example, the following code R6):
II_INSTALLATION=R6
Take note of your installation code: ______.
6. Check that all Vector processes are shut down. If there are processes that continue to run, see Check Shutdown Problems on Linux.
7. Restart Vector: Attempt once again to start up the installation by issuing the following command at the operating system prompt:
ingstart
8. If startup problems persist, continue the diagnostics described in Ingbuild on Linux or Detect Vector Startup Problems on Linux.
Ingbuild on Linux
The executable script ingbuild performs all the steps necessary to set up an installation. It checks system resources, installs shared memory and semaphores, configures DBMS server parameters, configures the logging and locking system, and starts all the required processes.
The ingbuild program is located in II_SYSTEM/ingres/utility. It makes use of numerous shell commands as well as the following Vector binary and shell executables:
• createdb
• ingstop
• ingstart
• ingprenv
• ingunset
• sql
One of the last things ingbuild does is call the ingstart script to start installation processes. When ingstart is called, it displays the message “Starting the Name Server process (iigcn).” If there are startup problems after this message has displayed, see Detect Vector Startup Problems on Linux.
Before you can diagnose a problem with ingbuild, you must identify which subroutine is failing. If you know which routine is failing and it is ingstart or one of the main installation processes (iigcn, iigcc, II_IUSV_nnn, dmfacp or iidbms), see the section below that addresses that executable.
Details on tracing are described in Bourne Shell -x Option.
Detect Vector Startup Problems on Linux
To diagnose Vector problems, use the following procedure.
1. Display which processes are running by using the csreport and operating system ps commands.
The csreport utility is described in Operating System Utilities and the ps command is described in Linux Operating System Utilities.
2. Verify that all required Vector system processes are running. The following processes (in the order they are started) are the minimum required for a complete installation:
iigcn
Name Server process
iigcc
Communications Server process (present only on sites with Vector Net)
iidbms (II_IUSV_nnn)
Recovery Server process
iigcd
Data Access Server process (present only if JDBC and/or .NET access is configured)
dmfacp
Archiver process
iidbms
DBMS Server process
Note: If the command ingprenv | grep II_CLIENT shows “II_CLIENT = true”, you need to run only the Name Server and Communications Server processes.
After a Vector database has been accessed, there will also be an iix100 process for that database. If no Vector databases have been accessed, it is normal to see no iix100 processes running. The system databases iidbdb and imadb are not considered Vector databases.
3. If ingstart does not complete successfully, try to identify the reason for startup failure. For example:
The problem is with ingstart. The ingstart script fails due to results of the checks it makes for sufficient resources and installation settings. If this is the reason for startup failure, correct the deficiency.
A process failed to start. If a process failed to start, continue on to the details sections on startup problems for that specific process.
Detect Vector Startup Problems on System Reboot (Windows)
To detect Vector startup problems on system reboot on Windows, follow these steps:
1. Check that the “Startup Type” for the “Ingres Intelligent Database” service has been set to “automatic” in the services dialog.
2. Check that the password specified for the service matches the installation owner user password.
3. Start the service manually.
4. If the service fails to start, run ingstart from the command prompt.
5. If the installation still does not start, contact technical support, as described in What You Need Before Contacting Actian Support.
Detect Vector Startup Problems on System Reboot (Linux)
To detect Vector startup problems on system reboot on Linux, follow these steps:
1. The most common cause of startup failure following a reboot is failure to include the startup command ingstart in the boot script for your machine. (The boot file is vendor-specific but can be named “/etc/rc” or “etc/rc.local”.) This file contains the commands that are to be executed immediately after a reboot.
Make sure that the following line appears in the boot script:
su userid -c "ii_system/ingres/utility/ingstart ii_system" /dev/console
where:
userid refers to the user that owns the installation
ii_system refers to the value of II_SYSTEM for your installation.
2. Make sure that /dev/kmem is readable to the user that owns the installation. If this is a security problem for your machine, you can add this user as a member of /dev/kmem’s group and make the /dev/kmem group readable.
Issue the following command at the operating system prompt:
chmod g+w /dev/kmem
The user that owns the installation must be able to read /dev/kmem or the kernel resource checks in ingstart fails.
3. Run ingstart. If the installation still does not start, contact technical support, as described in What You Need Before Contacting Actian Support.
Last modified date: 02/09/2026